Agentic AI Is Taking Over Engineering: From Code to Incidents and Databases
Published Jan 4, 2026
If messy backfills, one-off prod fixes, and overflowing tickets keep you up, here’s what changed in the last two weeks and what to do next. Vendors and OSS shipped agentic, multi-agent coding features late Dec (Anthropic 2025-12-23; Cursor, Windsurf; AutoGen 0.4 on 2025-12-22; LangGraph 0.2 on 2025-12-21) so LLMs can plan, implement, test, and iterate across repos. On-device moves accelerated (Apple Private Cloud Compute update 2025-12-26; Qualcomm/MediaTek benchmarks mid‐Dec), making private, low-latency assistants practical. Data and migration tooling added LLM helpers (Snowflake Dynamic Tables 2025-12-23; Databricks Delta Live Tables 2025-12-21) but expect humans to own a PDCVR loop (Plan, Do, Check, Verify, Rollback). Database change management and just‐in‐time audited access got product updates (PlanetScale/Neon, Liquibase, Flyway, Teleport, StrongDM in Dec). Action: adopt agentic workflows cautiously, run AI drafts through your PDCVR and PR/audit gates, and prioritize on‐device options for sensitive code.
AI Becomes the Engineering Runtime: PDCVR, Agent Stacks, Executable Workspaces
Published Jan 3, 2026
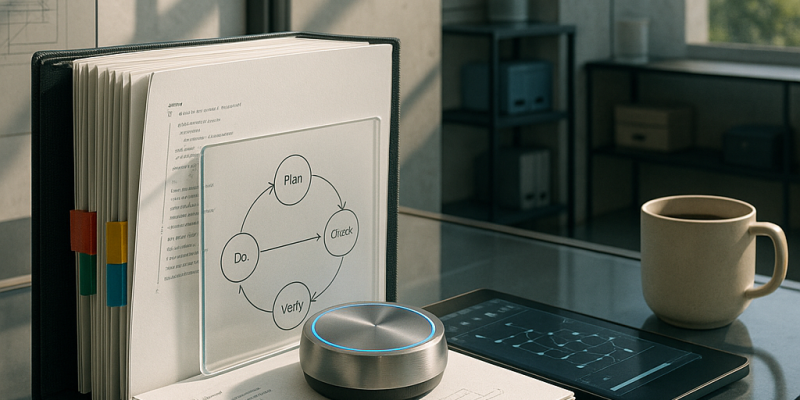
Still losing hours to rework and scope creep? New practitioner threads (Jan 2–3, 2026) show AI shifting from ad‐hoc copilots to an AI‐native operating model—and here’s what to act on. A senior engineer published a production‐tested PDCVR loop (Plan‐Do‐Check‐Verify‐Retrospect) using Claude Code and GLM‐4.7 and shared prompts and subagent patterns on GitHub; it turns TDD and PDCA ideas into a model‐agnostic SDLC shell that risk teams in fintech/biotech/critical infra can accept. Teams report layered agent stacks with folder‐level manifests plus a meta‐agent cut routine 1–2 day tasks from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours. DevScribe surfaces executable workspaces (databases, diagrams, API testing, offline‐first). Data backfills are being formalized into PDCVR flows. Alignment tax and scope creep are now measurable via agents watching Jira/Linear/RFC diffs. Immediate takeaway: pilot PDCVR, folder priors, agent topology, and an executable cockpit; expect AI to become engineering infrastructure over the next 12–24 months.
How AI Became the Engineering Operating System: PDCVR, Agents, Workspaces
Published Jan 3, 2026
In the past 14 days engineers shifted from treating LLMs as sidecar chatbots to embedding them as an operating layer—here’s what you’ll get: a concrete, auditable AI‐native engineering model and clear operational wins. A senior engineer published a Plan–Do–Check–Verify–Retrospect (PDCVR) workflow for Claude Code + GLM‐4.7 on Reddit (2026‐01‐03) with open prompts and agent configs on GitHub, turning LLMs into repeatable TDD‐driven loops. Teams add folder‐level priors and a prompt‐rewriting meta‐agent to keep architecture intact; one report cut small‐change cycle time from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours. DevScribe (2026‐01‐03) offers an offline, executable cockpit for DBs/APIs and diagrams. Practitioners also call for treating data backfills as platform features (2026‐01‐02) and using coordination agents to reduce the “alignment tax” (2026‐01‐02/03). The takeaway: the question isn’t which model, but how you design, instrument, and evolve the workflows where models and agents live.
How AI Became Your Colleague: The New AI-Native Engineering Playbook
Published Jan 3, 2026
If your teams are losing days to rework, pay attention: over Jan 2–3, 2026 engineers shared concrete practices that make AI a predictable, auditable colleague. You get a compact playbook: PDCVR (Plan–Do–Check–Verify–Retrospect) for Claude Code and GLM‐4.7—plan with RED→GREEN TDD, have the model write failing tests and iterate, run completeness checks, use Claude Code sub‐agents to run builds/tests, and log lessons (GitHub templates published 2026‐01‐03). Paired with folder‐level specs and a prompt‐rewriting meta‐agent, 1–2 day tasks fell from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours (20‐min prompt + a few 10–15 min loops + ~1 hour testing) (Reddit, 2026‐01‐02). DevScribe‐style executable, offline workspaces, reusable migration/backfill frameworks, alignment‐monitoring agents, and AI “todo routers” complete the stack. Bottom line: adopt PDCVR, agent hierarchies, and executable workspaces to cut cycle time and make AI collaboration auditable—and start by piloting these patterns in safety‐sensitive flows.
AI as an Operating System: Building Predictable, Auditable Engineering Workflows
Published Jan 3, 2026
Over the last 14 days practitioners zeroed in on one problem: how to make AI a stable, auditable part of software and data workflows—and this note tells you what changed and what to watch. You’ll see a repeatable Plan–Do–Check–Verify–Retrospect (PDCVR) loop for LLM coding (examples using Claude Code and GLM‐4.7), multi‐level agents with folder‐level manifests plus a prompt‐rewriting meta‐agent, and control‐plane tools (DevScribe) that let docs execute DB queries, diagrams, and API tests. Practical wins: 1–2 day tickets dropped from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours in one report (Reddit, 2026‐01‐02). Teams are also building data‐migration platforms, quantifying an “alignment tax,” and using AI todo‐routers to aggregate Slack/Jira/Sentry. Bottom line: models matter less than operating models, agent architectures, and tooling that make AI predictable, auditable, and ready for production.
Inside the AI-Native OS Engineers Use to Ship Software Faster
Published Jan 3, 2026
What if you could cut typical 1–2‐day engineering tasks from ~8 hours to ~2–3 while keeping quality and traceability? Over the last two weeks (Reddit posts 2026‐01‐02/03), experienced engineers have converged on practical patterns that form an AI‐native operating model you'll get here: the PDCVR loop (Plan–Do‐Check‐Verify‐Retrospect) enforcing test‐first plans and sub‐agents (Claude Code) for verification; folder‐level manifests plus a meta‐agent that rewrites prompts to respect architecture; DevScribe‐style executable workspaces that pair schemas, queries, diagrams and APIs; treating data backfills as idempotent platform workflows; coordination agents that quantify the “alignment tax”; and AI todo routers consolidating Slack/Jira/Sentry into prioritized work. Together these raise throughput, preserve traceability and safety for sensitive domains like fintech/biotech, and shift migrations and scope control from heroic one‐offs to platform responsibilities. Immediate moves: adopt PDCVR, add folder priors, build agent hierarchies, and pilot an executable workspace.
How AI Is Rewiring Software Engineering: PDCVR, Agents, Executable Workspaces
Published Jan 3, 2026
What if a typical 1–2 day engineering task drops from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours? In the last two weeks practitioners (Reddit threads dated Jan 2–3, 2026) showed how: an AI‐native SDLC loop called PDCVR (Plan‐Do‐Check‐Verify‐Retrospect) built on Claude Code and GLM‐4.7, folder‐level priors plus a prompt‐rewriting meta‐agent, executable workspaces like DevScribe, repeatable data‐migration/backfill patterns, and tools to surface the “alignment tax.” PDCVR forces repo scans, TDD plans, small diffs, sub‐agents (open‐sourced in .claude on GitHub, Jan 3, 2026) to run builds/tests, and LLM retrospectives. Measured gains: common fixes go from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours with 20‐minute prompts and short PR loops. Bottom line: teams in fintech, healthtech, trading and regulated sectors should adopt these operating models—PDCVR, multi‐level agents, executable docs, migration frameworks—and tie them to speed, quality, and risk metrics.
AI as Engineer: From Autocomplete to Process-Aware Collaborator
Published Jan 3, 2026
Your team’s code is fast but fragile — in the last two weeks engineers, not vendors, published practical patterns to make LLMs safe and productive. On 2026‐01‐03 a senior engineer released PDCVR (Plan‐Do‐Check‐Verify‐Retrospect) using Claude Code and GLM‐4.7 with prompts and sub‐agents on GitHub; it embeds planning, TDD, build verification, and retrospectives as an AI‐native SDLC layer for risk‐sensitive systems. On 2026‐01‐02 others showed folder‐level repo manifests plus a prompt‐rewriting meta‐agent that cut routine 1–2‐day tasks from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours. Tooling shifted too: DevScribe (site checked 2026‐01‐03) offers executable, offline docs with DBs, diagrams, and API testing. Engineers also pushed reusable data‐migration patterns, highlighted the “alignment tax,” and prototyped Slack/Jira/Sentry aggregators. Bottom line: treat AI as a process participant — build frameworks, guardrails, and observability now.
AI Is Becoming the Operating System for Software Teams
Published Jan 3, 2026
Drowning in misaligned work and slow delivery? In the last two weeks senior engineers sketched exactly what’s changing and why it matters: AI is becoming an operating system for software teams, and this summary tells you what to expect and do. Teams are shifting from ad‐hoc prompting to repeatable, auditable frameworks like Plan–Do–Check–Verify–Retrospect (PDCVR) (implemented on Claude Code + GLM‐4.7; prompts and sub‐agents open‐sourced, Reddit 2026‐01‐03), cutting error loops with TDD and build‐verification agents. Hierarchical agents plus folder manifests trim a task from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours (20‐minute prompt, 2–3 feedback loops, ~1 hour testing). Tools like DevScribe collapse docs, queries, diagrams, and API tests into executable workspaces. Data backfills need platform controllers with checkpointing and rollforward/rollback. The biggest ops win: alignment‐aware dashboards and AI todo aggregators to expose scope creep and speed decisions. Immediate takeaway: harden workflows, add agent tiers, and invest in alignment tooling now.
AI-Native SDLC: PDCVR, Agentic Workflows, and Executable Workspaces
Published Jan 3, 2026
Tired of AI “autocomplete” causing more rework? Reddit threads from 2026‐01‐02–03 show senior engineers wrapping LLMs into repeatable processes—here’s what matters for your org. They describe a Plan–Do–Check–Verify–Retrospect (PDCVR) loop (Claude Code + GLM‐4.7) that enforces TDD stages, separate build/verification agents, and prompt‐template retrospectives for auditability—recommended for fintech, biotech, and safety‐sensitive teams. Others report folder‐level manifests plus a prompt‐rewriting meta‐agent cutting 1–2‐day tasks from ~8 hours to ~2–3 hours (3–4× speedup). Tool trends: DevScribe’s “executable docs,” rising need for robust data‐migration/backfill frameworks, and coordination‐aware agent tooling to reduce weeks‐long alignment tax. Engineers now demand reproducible evals, exact prompts, and task‐level metrics; publish prompt libraries and benchmarks, and build verification and migration frameworks as immediate next steps.